A blood test
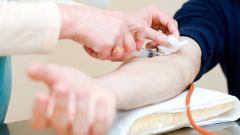
The blood analysis allows to confirm the diagnosis of cancer and to determine the approximate location of the malignancy. Determination of the extent of the disease and its localization is carried out based on specific tumor markers, i.e. substances that are released only in the tumour cells and enter directly into the blood.
Also the calculation takes the number of leukocytes in the blood, which is increased in the presence of a nodule. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate will also be high. The level of hemoglobin in cancer patients is significantly reduced. It is worth noting that the blood test does not diagnose the tumor, but only enables the physician to obtain a General picture of the disease. The blood composition may change depending on the patient's lifestyle, health status, and the presence of other diseases.
For more accurate diagnosis can be carried out urine analysis on the basis of which is determined by the amount of protein secreted in the patient, and the presence of hematuria (blood in urine). Excess levels of protein may indicate problems with the kidneys or cardiovascular system. Blood in the urine may indicate the presence of benign or malignant tumors, infections or structural problems of organs.
Endoscopy
During the endoscopy, the patient is injected a plastic tube on the end of which is a small camera with a light bulb. The image is transmitted to a monitor through which the doctor is able to see the tumor and take a tissue sample (biopsy) for further analysis. The advantage of endoscopy is the ability to see the tumor, determine its exact location. Depending on the body part where the research may apply different techniques. Thus, colonoscopy allows to see the cancer of a direct gut, and laparoscopy provides the opportunity to examine the abdominal cavity through a small incision.
Biopsy
A tissue sample for biopsy is taken in the process of endoscopy, and directly using a special needle, if the doctor knows the exact location of the tumor. Before the procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Long and thin needle is inserted into the area of the tumor. With a special syringe runs a fence of fluid from the tumor to send to the lab. Based on these results, we can prescribe treatment.
Other methods
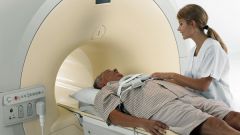
Also used for diagnostic x-ray, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasonography (us). These methods allow to obtain information on the accurate location of tumor, to establish its size. These technologies are used in the case when to determine an approximate location of the tumor other methods is not possible.