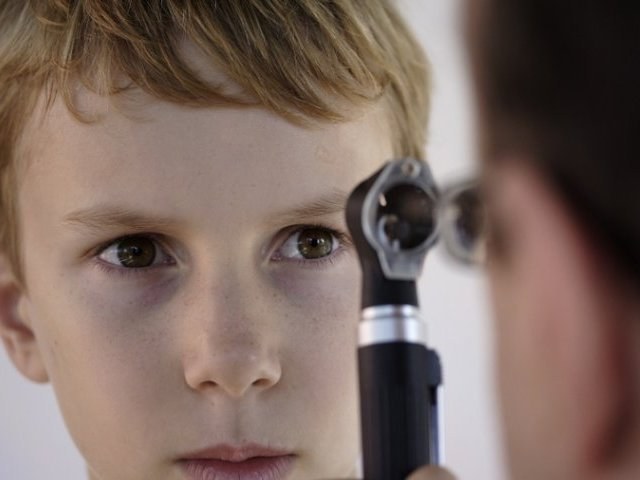
Especially the study of the fundus in children
The fundus of the eye in children check with the purpose of identifying eye diseases, pathologies of blood vessels, brain, and signs of hypertension. For ophthalmoscopy used several methods. Most often the physician uses the Ophthalmoscope mirror, some experts prefer electronic device. In some cases the research is conducted by the method of fluorescent antigraffio (FAGD).
Perform ophthalmoscopy in a dark room. Left and slightly behind the patient set frosted lamp having a power of about 100 watts. The doctor is at a distance of 30-40 cm from the patient and right eye looks through the hole of the eye mirror of the Ophthalmoscope, directing the pupil of the patient beam of light. Light enters eyesand then reflected from the pigment epithelium and the choroid.
When checking the fundus of the eye in children appears a number of difficulties, because young patients are not able to overcome the reflex and close my eyes to protect from light. Therefore, in order to improve pupil before the procedure they buried 1% solution of "Homatropine". If a child cannot cope with zamurovannye, the doctor applies the eyelid retractor. Older children are asked to focus on some picture, object.
The fundus of the eye in children: norm and pathology
The fundus of the eye in children is different from the fundus of an adult. Newborns in norm it has a light yellow color, the optic nerve disc pale pink with a slight gray tint, no macular reflex. Greyish tint of the optic disc is preserved up to 2 years.
Born in asphyxia of children during the inspection will be revealed small hemorrhages, are irregular in shape. If these areas are located along the arterioles, they dissolve on the 6th day of life. Hemorrhage with preretinal character, persist longer and can be repeated. If the inspection revealed a sharp pallor of the temporal half of the disc, this indicates a congenital atrophy of the optic nerve. In this case the boundaries are very clear, there is a narrowing of the arteries. In different brain lipoidosis (hereditary abnormalities of lipid metabolism) in the region of the macula (the Central part of the retina) detected by the spot of cherry-red color.
Normally, the retina can have different shades, depending on the volume of blood circulating in the vessels. In some cases the pigment epithelium, located between the upper and the capillary layer, attached retina dark red or dark brown color. By reducing the amount of pigment effect appears parquet fundus: the retina image has wide stripes, alternating with dark patches. Normal optic nerve looks like a round pink spot. It is located on the red background of the fundus and has pale temporal part. The color of the disk will depend on the number of capillaries with age it becomes paler. The hue can affect the development of hypertension and other pathologies, as well as the accumulation of pigment. If the inspection found that the disk is surrounded by a semicircle, this would indicate a detachment from the edge of the nerve of the choroid.