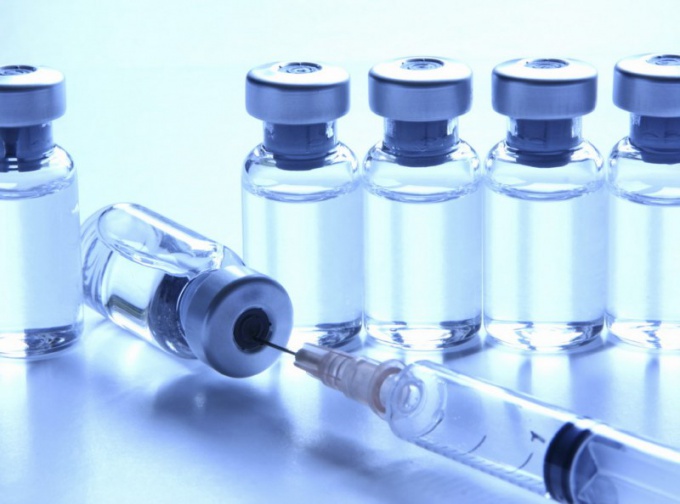
Vaccination - the most important section of modern medicine. What vaccinations mankind owes to the fact that many diseases which were once extinct in the whole country, today remained in the distant past. Thanks to vaccination, the modern man finds out about the virus of smallpox or plague only from books and medical journals. Some vaccinations against the most common diseases a person receives immediately after birth, according to the relevant calendar.
The first in the history of medicine, the vaccine was created in the XVIII century. Edward Jenner, a British scientist who produced a vaccine against smallpox using vaccinia virus extracted from the body of sick animals. Cow pox did not pose a danger to humans, however, contributed to the development of specific antibodies that protect people from disease. Thanks to Jenner's vaccine, the incidence of smallpox began to decline. The next stage in the history of vaccination is associated with the name of the famous scientist Louis Pasteur. He continued the studies of Jenner and began to create vaccines based on attenuated microorganisms.
Thus, a vaccine is in the microorganisms or their toxins, pre-weakened or killed, so as not to cause harm to the human body. Vaccines stimulate the body's defenses, promote the development of its own antibodies and adaptation of the immune system to certain types of pathogens.
If the response to vaccination, the body begins to produce antibodies independently, therapeutic serum is a set of ready-made antibodies. After the introduction of serum does not require additional time to develop a full immunity. Often injected with the serum do in the case of direct infection, when preventive measures are taken too late.
And vaccines, and serum are introduced by injection. It is believed that the serum is different from the vaccine because it rarely causes allergic reactions in a patient. However, the physician must carefully examine the condition of the patient before administration of the drug and to observe all the rules to avoid possible complications.
The history of vaccination began in the XVIII century, when British scientist Edward Jenner invented the world's first vaccine against smallpox.Among the many vaccinations that we face throughout life, there are drugs of different types. Most often, the doctor makes the patient a vaccine or curative serum. Despite the fact that vaccines and serums are methods of preventing infections, they have significant differences.
What is a vaccine?
The first in the history of medicine, the vaccine was created in the XVIII century. Edward Jenner, a British scientist who produced a vaccine against smallpox using vaccinia virus extracted from the body of sick animals. Cow pox did not pose a danger to humans, however, contributed to the development of specific antibodies that protect people from disease. Thanks to Jenner's vaccine, the incidence of smallpox began to decline. The next stage in the history of vaccination is associated with the name of the famous scientist Louis Pasteur. He continued the studies of Jenner and began to create vaccines based on attenuated microorganisms.
Thus, a vaccine is in the microorganisms or their toxins, pre-weakened or killed, so as not to cause harm to the human body. Vaccines stimulate the body's defenses, promote the development of its own antibodies and adaptation of the immune system to certain types of pathogens.
What is whey?
If the response to vaccination, the body begins to produce antibodies independently, therapeutic serum is a set of ready-made antibodies. After the introduction of serum does not require additional time to develop a full immunity. Often injected with the serum do in the case of direct infection, when preventive measures are taken too late.
Example serum quick action serves as a tetanus shot. Tetanus toxoid is administered immediately after injury to the skin, to prevent the development of disease in case of infection.
And vaccines, and serum are introduced by injection. It is believed that the serum is different from the vaccine because it rarely causes allergic reactions in a patient. However, the physician must carefully examine the condition of the patient before administration of the drug and to observe all the rules to avoid possible complications.