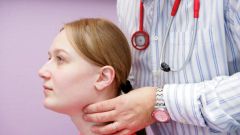
Palpation of the thyroid gland
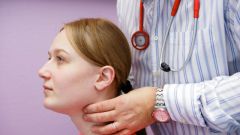
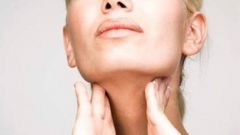
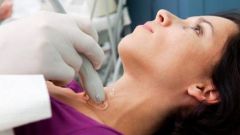
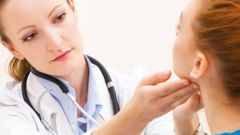
In some diseases not only disrupted the function gland, but also changes of a physiological nature. The thyroid gland can increase in size in the tissues of the body can receive the components, seals and signs of goiter. For the initial diagnosis, the doctor-endocrinologist uses this method of examination, as palpation. It is a simple procedure, the doctor asks the patient to make the normal SIP and swallow with the fingers palpate the neck. If the thyroid is severely affected, palpation the patient may feel severe pain. Palpation allows only tentative conclusions, for a more accurate diagnostics using instrumental and laboratory methods of research.
Instrumental diagnostics of the thyroid gland
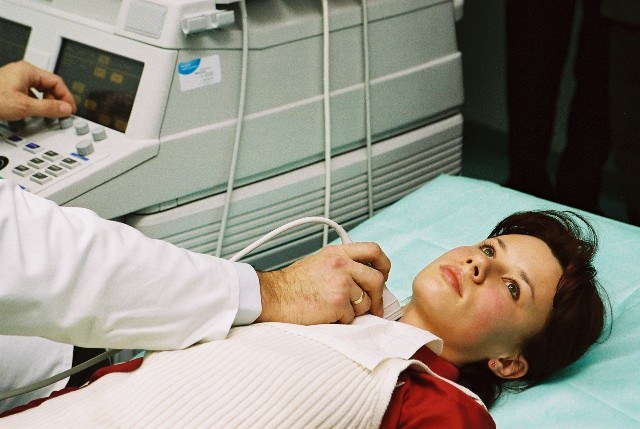
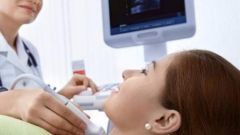
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland allows to assess the structure of organ tissue. With the help of ultrasound can determine the volume of the breast, to study the blood flow in the organ tissue, to detect knots and measure their size. The direction of ultrasound of the thyroid gland gives endocrinologist if the palpation was detected any changes.
If the results of the ultrasound were discovered large nodules in the tissues of the gland, the patient can be assigned to needle biopsy. This survey allows to identify the nature of the lesion and to exclude cancer. Doctor using a thin needle penetrates into the cavity of goiter and takes tissue samples. Sure puncture is performed under ultrasound guidance.
Malignant tumours in the thyroid scintigraphy is carried out. This survey enables to identify the prevalence of cancer process and to detect metastases. In the process of this survey in the human body is injected a certain amount of radioactive substances. At the moment of absorption of radioactive iodine in tissue of the body to define the affected area.
Laboratory diagnosis of thyroid
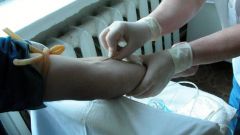
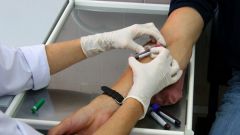
By analyzing blood from a vein on hormones, it is possible to determine the functional state of the gland, that is, to understand how well the organ performs its function. The blood sample is taken strictly on an empty stomach. In laboratory diagnosis is most often determined the level of TSH, T3 and T4.
TSH is thyroid stimulating hormone which produces the pituitary gland, this hormone regulation of the endocrine function of the thyroid gland. The TSH level will depend on the level of thyroid hormones. If the level of thyroid hormones decreases, the pituitary gland begins to actively produce thyroid hormone and TSH levels in the blood. If the thyroid gland produces excess hormones, the TSH level in the blood is below normal.
T3 – triiodothyronine is a hormone secreted by the thyroid gland. Analysis at the level of T3 is assigned in cases of suspected hyperthyroidism. T4 is a hormone thyroxine, which is also the thyroid hormones. This hormone is more important for determining an imbalance of hormones than T3. Elevated levels of T4 indicate hyperthyroidism and low for hypothyroidism.