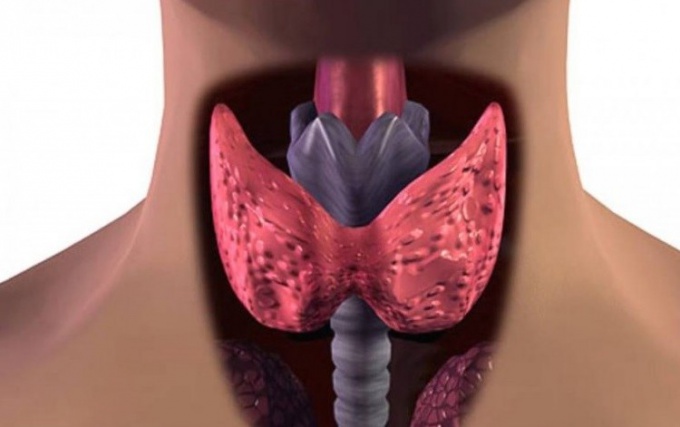
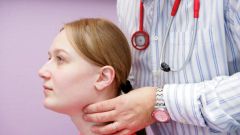
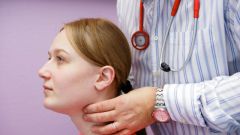
The size and weight of the gland varies considerably. On average, a healthy adult it weighs about 20 grams. The thyroid gland produces two important hormones – thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones regulate the function of gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, mental and sexual activity, metabolic processes of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Also, the thyroid gland secretes into the bloodstream the hormone calcitonin, which is involved in the regulation of calcium levels. The functioning of the thyroid gland depends on the amount of iodine in the body. For the normal functioning of the body a person should get per day about 150-200 mg of iodine. The best natural sources of this element are considered saltwater fish, seafood, seaweed, persimmons, Bulgarian pepper. To find out whether there is enough iodine your thyroid, draw on the inner part of the forearm iodine mesh and notice when she will disappear. Normally, the picture must remain on the skin for more than 2 hours, if it disappears before - iodine are lacking.
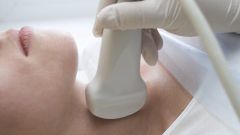
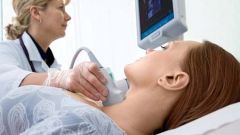
When the thyroid gland ceases to cope with its functions, the body begins hormonal chaos - there is irritability, worsening memory, suffers from the immune system, there is a hand tremor, thinning hair, edema, women have disturbed menstrual cycle, reduced the probability of conception, complicated pregnancy process. If there are such changes in the body, you need to immediately see a specialist - endocrinologist. He will conduct the necessary research and diagnosis.
Dysfunction of the thyroid can manifest in the increase (hyperthyroidism) or decrease (hypothyroidism) hormone production. In our country, the most common is hypothyroidism, which occurs when a lack of iodine in the body. The thyroid gland begins to produce enough hormones, which leads to a decrease in motor activity, drowsiness, weakness, impaired attention, impaired judgement, obesity, increased cholesterol levels, impaired potency, obesity. External symptoms of hypothyroidism – dry pale skin, hair loss, brittle nails. In order to capture more iodine from the blood, the thyroid gland starts to increase and gradually grows goiter. Without treatment, the goiter may reach several kilograms.
The reverse situation, when the thyroid hormones are produced more than normal, is called hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis. There is a boost metabolism, nervousness, frequent palpitations, excessive sweating, tremor, poor sleep, fatigue, decrease in libido and potency, in advanced cases, proptosis (protrusion of the eyeball). Patients may have appetite, but lose weight. Goiter can also appear in hyperthyroidism, in this case it is a diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland - Graves ' disease.
Hypothyroidism, in most cases, irreversible. Patients have to take artificial thyroid hormones for life. The dose of hormonal drugs should be determined by the doctor. Hyperthyroidism requires treatment, otherwise the condition progresses, there is a change in the heart muscle, disturbances of cardiac rhythm, liver damage. Without treatment death may occur from heart failure or thyrotoxic crisis. Treatment of hyperthyroidism is complex and lengthy. Prescribers, inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones. In rare cases, radioactive iodine, which kills the cells of the thyroid gland. In severe cases, undergoing a complete surgical removal of the thyroid gland.
Thyroid disease
When the thyroid gland ceases to cope with its functions, the body begins hormonal chaos - there is irritability, worsening memory, suffers from the immune system, there is a hand tremor, thinning hair, edema, women have disturbed menstrual cycle, reduced the probability of conception, complicated pregnancy process. If there are such changes in the body, you need to immediately see a specialist - endocrinologist. He will conduct the necessary research and diagnosis.
Dysfunction of the thyroid can manifest in the increase (hyperthyroidism) or decrease (hypothyroidism) hormone production. In our country, the most common is hypothyroidism, which occurs when a lack of iodine in the body. The thyroid gland begins to produce enough hormones, which leads to a decrease in motor activity, drowsiness, weakness, impaired attention, impaired judgement, obesity, increased cholesterol levels, impaired potency, obesity. External symptoms of hypothyroidism – dry pale skin, hair loss, brittle nails. In order to capture more iodine from the blood, the thyroid gland starts to increase and gradually grows goiter. Without treatment, the goiter may reach several kilograms.
The reverse situation, when the thyroid hormones are produced more than normal, is called hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis. There is a boost metabolism, nervousness, frequent palpitations, excessive sweating, tremor, poor sleep, fatigue, decrease in libido and potency, in advanced cases, proptosis (protrusion of the eyeball). Patients may have appetite, but lose weight. Goiter can also appear in hyperthyroidism, in this case it is a diffuse enlargement of the thyroid gland - Graves ' disease.
Treatment of pathologies of the thyroid gland
Hypothyroidism, in most cases, irreversible. Patients have to take artificial thyroid hormones for life. The dose of hormonal drugs should be determined by the doctor. Hyperthyroidism requires treatment, otherwise the condition progresses, there is a change in the heart muscle, disturbances of cardiac rhythm, liver damage. Without treatment death may occur from heart failure or thyrotoxic crisis. Treatment of hyperthyroidism is complex and lengthy. Prescribers, inhibiting the production of thyroid hormones. In rare cases, radioactive iodine, which kills the cells of the thyroid gland. In severe cases, undergoing a complete surgical removal of the thyroid gland.