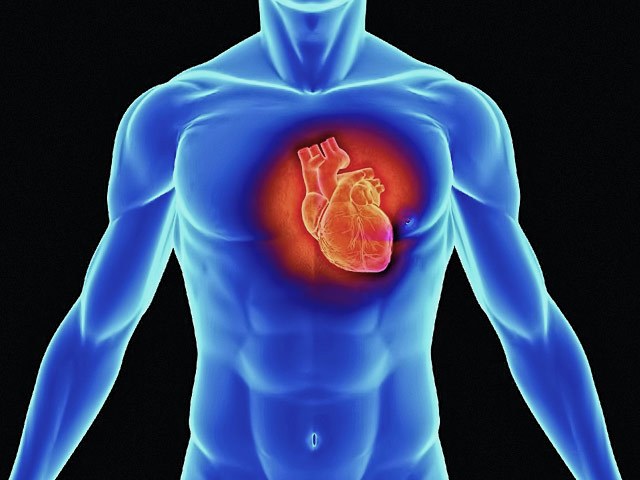
Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a heart rate more than 100 beats per minute. It may occur as a result of increased activity of the region which is above the ventricle – this is called supraventricular tachycardia. There are five types of supraventricular tachycardia: atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, syndrome Wolff-Parkinson-white and atrioventricular nodal reciprocal tachycardia.
Supraventricular tachycardia often occurs in people with perfectly healthy hearts who do not even notice heart palpitations.
Atrial flutter is typically called age-related heart disease and is characterized by internal discomfort, frequent heartbeat, shortness of breath, fatigue and a feeling of tightness in the chest. However, the most common cause of palpitations is atrial fibrillation, which develops for no apparent reason. Its symptoms begin to appear with age and represent the intermittent pulse, dizziness, shortness of breath and irregular heartbeat frequent. If the heart beats too fast, people can lose consciousness.
Problems with the heart ventricles
Heart rate exceeding 120 beats per minute, is called ventricular flutter. This condition is dangerous to their excessively rapid contraction in which the ventricles do not have time to fill with blood and the heart pumps into the vascular system a very small amount of blood rich in vital oxygen. Most often, ventricular flutter occurs in patients with heart disease who suffered a heart attack or suffer from narrowing of the coronary arteries.
Flutter heart ventricles traditionally treated such procedures as defibrillation, is performed in a hospital.
If the heart beats with a frequency of 300 beats per minute or more, the diagnosis "ventricular fibrillation". The steady conservation of this state, the patient loses consciousness from collapse of the cardiovascular system and is experiencing oxygen deprivation. In the untimely appeal in an ambulance a result of ventricular fibrillation may occur irreversible damage to the brain and other internal organs, and death.
To control the palpitations, you need to identify and cure the disease that provokes its repetition. In certain severe cases, doctors prescribe the patient the implantation of cardioverter-defibrillator.