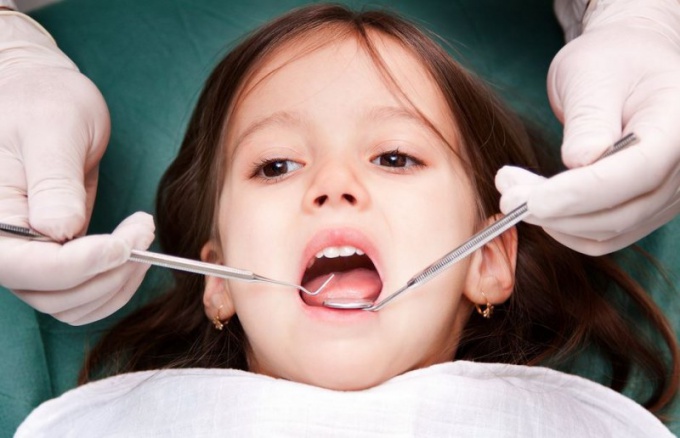
The structural features of a baby tooth
At the histological and anatomical structure of the tooth is similar to constant. And just as constant, they differ from each other by their purpose and form.
Each tooth is covered with enamel. It is 96% percent consists of mineral and calcium salts and is the most durable of all tissues. The enamel has a shell, called the cuticle. Over time, the chewing surface of the tooth it is erased.
Immediately underneath the enamel is dentin. This bone mineralized tissue that is the basis of the tooth. In strength it ranks second, behind the enamel. The dentin surrounds the cavity of tooth and root channels.
The internal cavity of the tooth is filled with pulp. It is a soft spongy tissue. It is located in the crown of the tooth and in the root. The pulp is penetrated by numerous blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves.
The root of the baby tooth eventually resolved. This happens to a permanent tooth was easier to displace the tooth.
Nerves are milk and permanent tooth?
Adults often think that baby teeth do not have nerves, but this is erroneous opinion. Each milk tooth is a nerve, and it is its important constituent.
Nerves milk and permanent tooth are completely unrelated. In the event of pulpitis milk tooth, you must immediately go to the dentist, but do not be afraid, that the pulpit will affect the permanent tooth. But if you do not treat baby teeth, the inflammatory process can penetrate into the bone tissue and stop the process of formation of permanent teeth.
In the treatment of tooth dentists consider age of the patient. Closer to six years the roots of the milk teeth are absorbed, respectively, in the treatment there is a high risk of injury to the permanent tooth. Therefore, the removal of the nerve channels are processed only in the mouth parts. Treated the tooth with a special solution that allows the tooth to survive until the change permanent.
Differences deciduous teeth from constant
All 20 deciduous teeth and the number of permanent teeth varies from 28 to 32. Are baby teeth more upright than the permanent ones. The dimensions of the crowns of deciduous teeth and permanent, as well as the roots, are different. Milk teeth is less than that associated with the emergence of milk teeth. They appear at an early age, when the jaw of the child is small. The thickness of enamel and dentin from a baby tooth is much thinner than permanent tooth. But the amount of pulp of a deciduous tooth more. The tooth is not difficult and mostly it happens in a natural way. But to remove the permanent tooth need dental services.