Indications and contraindications to fibrobronchoscopy
The procedure is performed for diagnostic purposes to determine the causes of hemoptysis and major changes in the bronchi, detected by x-ray. This method has been successfully used in cases of suspected oncological pathology or inflammatory process, for extraction of foreign bodies, examination of the bronchi is curved with a narrow lumen and administering medicines. In addition, fiber-optic bronchoscopy is used to biopsy – otsyrevanija pieces of tissue of the bronchi, which allows you to set the diagnosis and prescribe optimal treatment.
Among the contraindications to the study – asthma, pneumonia in acute cerebrovascular disease, myocardial infarction, and severe forms of cardiovascular and cardiopulmonary insufficiency.
How to prepare for the study
Fiber-optic bronchoscopy is usually performed in the morning on an empty stomach. If the procedure is scheduled for a different time, you should take a break from eating for at least 8 hours. Before the examination the patient should inform the doctor about chronic diseases or allergic reactions. It is advisable to carry medical records with lab results and previous endoscopic examinations (repeated examination).
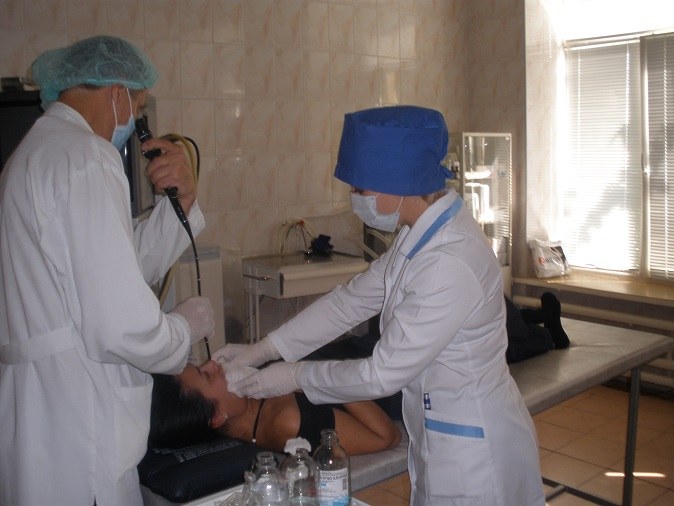
Technique of bronchoscopy
During the procedure, the patient sits or lies on a couch. For the study applies the bronchofiberscope is a complex instrument equipped with a photo - or video camera.
We first performed local anaesthesia of the nasopharynx and vocal cords a 10% solution of Lidocaine in the form of a spray, and the trachea and bronchi obezbolivatmi 2% solution.
The tube of the apparatus is introduced into the lower nasal passage, then to the larynx, trachea and bronchi, followed by their assessment. The procedure does not hinder the breathing of the patient, but he can experience the feeling of a foreign body in the larynx, causing cough.
The study lasts for a few minutes after the discomfort disappear.
Possible complications
Typically, fiber-optic bronchoscopy excludes unwanted effects and poses minimal risk to the patient. In rare cases there is a pneumothorax (accumulation of air in pleural cavity), pneumonia, perforation of the bronchial wall, bleeding, heart rhythm disturbances and postbronchoscopy fever.