Characterization of brain cancer
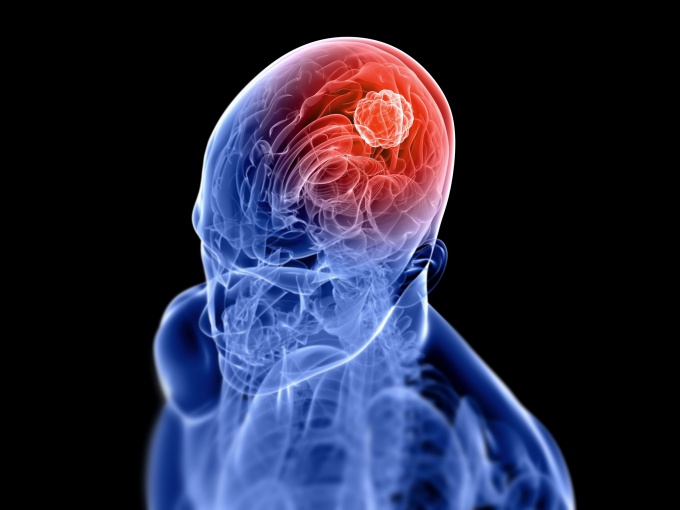
A brain tumor is a tumor that may have a different etiology and may vary by class: primary and secondary.
Primary tumors arise in the brain, and do not metastasize from other organs. Benign tumors are localized in one part of the brain, however, they do not destroy the surrounding tissue, do not give metastases and do not spread in the human body. The purity of the tumor is determined by slow growth rates. And usually, the symptoms depend on the location. So, it may be expressed in the attacks of headaches, seizures, decreased hearing or vision. Quite often these tumors are asymptomatic and detected by chance in the survey on magnetic resonance imaging. In some cases, removal of the tumor impossible. For example, when the proximity with the vital structures of the brain. Very often, after removal of the disease gives a relapse. Then radiation therapy or re-resection.
Malignant neoplasms. A tumor of this kind is able to spread to nearby healthy cells and destroy them. For cancer of the brain pathology is devastating not only to the brain but also other organs and cells of the body. Malignant tumors grow very quickly and are felt only in the last stages, when their removal is not possible. If treated brain cancer? Possible with early diagnosis and timely treatment.
Secondary tumor is called the spread of cancer cells from other affected organs. Three times more often than primary found secondary cancer of the brain. How I live with it, depends on how active brain metastases attack. As a rule, metastases penetrate into the brain in cancer of the breast, skin, kidney, lungs. Treated cancer of the brain during the secondary process? In this type the chances are negligible, as has already metastasized.
Varieties of brain tumors
Depending on the location there is the following classification of tumors:
Glioma. The tumor develops from glial cells of the brain. The cancer has 4 stages and is most common in men and children. For gliomas include oligodendroglioma, ependymoma and mixed glioma.
Meningioma is mostly a benign.
Medulloblastoma – a malignant form of neoplasm, which affects mostly children.
Lymphoma of the Central nervous system – etiology of malignant neoplasm that affects the lymphatic system.
A tumor on the pituitary adenoma. A tumor with benign course.
A tumor of the pineal body, epiphysis. A malignant tumor, which makes itself felt only at stage 4, when the operation of resection is impossible to produce. Is there a cure for brain cancer with this course? The chances of recovery are small.
Hemangioblastoma – damage of blood vessels of benign tumors.
Neuroma – lesion in the auditory nerve, benign tumor. Tumors of the spinal cord.
Causes of brain cancer
The exact causes of brain cancer is not established yet, but there are a few increased risk factors for its occurrence. These include:
- Paul. Men suffer more often than women.
- Age. Most often a brain tumor can be observed in people over 65. It is characteristic that at risk are the children under 8 years.
- Ethnicity. Compared to other members of the European race in 2 times more likely to get cancer. For example, the glioma is typical for people with white skin.
- Health. Important cause of cancer of the brain - diseases of the immune system. For example, HIV infection, transplantation of organs and tissues, post-chemotherapy.
- Chemical. People working in hazardous industries suffer from brain tumors more often.
- Heredity. Your risk is higher if someone of your relatives had cancer of the brain.
- Environment and radiation. People working with radioactive materials, are at risk for tumors. Researchers have recently come to the conclusion that the development of brain tumors may affect appliances and proximity to high-voltage transmission lines, as they generate electromagnetic fields that can alter the structure of cells. But cell phones and mobile phones recognized as safe and do not affect the structure of the gray matter.
How does brain cancer
The symptoms of brain cancer are varied and depend on tumor location. When the primary (focal) signs of the disease is compression and destruction of brain tissue in the region of the tumor. When the tumor progresses, there is General cerebral symptoms, which impaired hemodynamics and increased intracranial pressure.
Simptomatic
Following the defeat, which depend on the localization process:
Movement disorders in the form of paralysis and paresis. Marked reduction of muscle activity, impaired function of limbs. Violation of the sensitivity. In humans it is reduced or disappears. He does not respond to external stimuli such as cold, pain or tactile touch. Very often there is an impaired ability to determine the position of the limbs relative to the body. Violation of speech and hearing, occurs when the defeat of the auditory nerve.
Epileptic seizures. Observed in stagnant foci of excitation in the cerebral cortex.
Blurred vision. When compressed by a tumor of the optic nerve or the location of the corpora quadrigemina there comes a partial or complete loss of vision.
A speech disorder. The absence or partial presence of slurred speech. Hormonal imbalance.
Autonomic dysfunction: fatigue, constant fatigue, dizziness, fluctuations in blood pressure and pulse.
Disorder of coordination. In lesions of the cerebellum gait changes, the patient can not make precise movements. Broken memory, there is irritability, changes in character.
With the progression of the process there is complete confusion and loss of self.
Non-focal neurological symptoms
The symptoms occur due to increased intracranial pressure and compression of brain tumor.
Headaches. They are continuous and intense and almost never cropped.
Nausea and vomiting pursues the patient constantly, as there is a constant compression of the vomiting center in the midbrain. Dizziness appears when the pressure of the tumor on the cerebellum.
Treatment of brain cancer
All patients proceeding with this diagnosis in a hospital, wondering whether treated brain cancer? Quality treatment involves a set of expensive technologically advanced clinical interventions. Not in all cases, unfortunately, it is curable. All depends on the degree of brain cancer and its type.
Symptomatic treatment
The next group of drugs is much easier the patient's condition, but do not eliminate the main cause of the disease. Glucocorticosteroid help to reduce cerebral symptoms. NSAIDs help with pain relief. Narcotic analgesics are used when a strong pain syndrome, vomiting and psychomotor agitation.
Surgical treatment
This is the most effective way of treating cancer. Neurosurgeon excised the tumor in healthy tissue. It all depends on the location and stage of the tumor. Practically the operation is effective only on 1 stage. The next stages of the disease treatment is different. In particular, radiation therapy is also used.
Radiation therapy
Such treatment is needed to stop the growth of abnormal cells. It is conducted before, during and after surgery.
Chemotherapy
Typically such treatment is prescribed when the tumor is the last stage and inoperable. The dose and form of specific drugs for each patient is calculated individually.
Forecast
Brain cancer is treated, but only if detected early. After completing courses of treatment recovery occurs in 60-80%. If people applied too late, the chance of recovery is less than 30%.