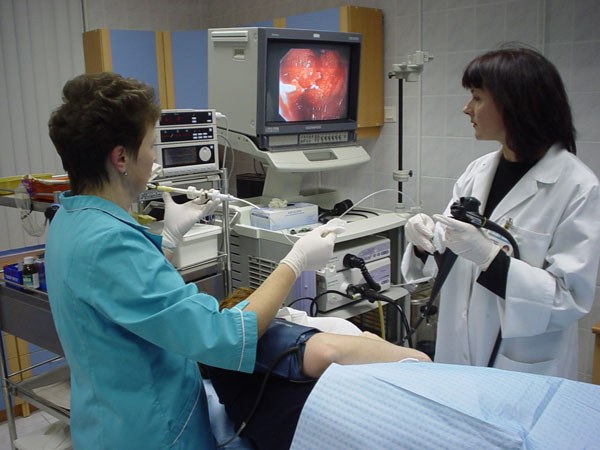
Duodenopathy is a symptom of inflammation of the duodenum, detectable only when fibrogastroduodenoscopy. This diagnostic procedure is to visualize the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract. Duodenopathy endoscopically evident hyperemia and edema of the mucosa of the colon.
Patients with duodenopathy recommended split meals in small portions four times a day with a predominance of protein foods and limiting simple carbohydrates.
The main goal of the diet is to limit foods that negatively affect the mucosa of the duodenum.
Patients are eating vegetable soups with pureed cereals and cream, boiled fish or meat, cooked boiled eggs, baked vegetables and fruits. The daily diet is recommended to enrich dairy and sour-milk products: yogurt, cottage cheese, sour cream, milk, butter. Healthy drinks are infusions and decoctions of herbs, weak green or black tea, and fruit juices rich in vitamin C.
Patients should limit the intake of honey, sugar, salt, confectionery, sweet pastries. There are a number of strictly prohibited products: canned food, alcohol, smoked food, fatty meats and fish, coffee, condiments, ice cream, very hot or very cold food.
With strict adherence to this diet within two months, the hyperemia and edema of the mucosa of the intestine become less pronounced, and the health of patients significantly improved.
To reduce the severity of endoscopic signs of duodenopathy using such medications, like proton pump inhibitors. These funds reduce, and then inhibit the production of hydrochloric acid. These include derivatives of omeprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole. Not less important are histamine receptors on the foundations of ranitidine, famotidine, cimetidine.
Among drugs of great importance are blockers of cholinergic receptors and non-selective m-anticholinergics. This aid, which also reduces the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Antacids required to protect the mucosa and recovery.
Antibiotic therapy aimed at the destruction of one of the main etiological factors of duodenopathy — microorganism Helicobacter pylori. The drugs of choice are amoxicillin, tetracycline, clarithromycin.
The duration of treatment is strictly individual. Monitoring the healing of pathology is carried out using a repeated fibrogastroduodenoscopy. With the disappearance of all endoscopic signs of inflammation the treatment is completed.
Diet of duodenopathy
Patients with duodenopathy recommended split meals in small portions four times a day with a predominance of protein foods and limiting simple carbohydrates.
The main goal of the diet is to limit foods that negatively affect the mucosa of the duodenum.
Patients are eating vegetable soups with pureed cereals and cream, boiled fish or meat, cooked boiled eggs, baked vegetables and fruits. The daily diet is recommended to enrich dairy and sour-milk products: yogurt, cottage cheese, sour cream, milk, butter. Healthy drinks are infusions and decoctions of herbs, weak green or black tea, and fruit juices rich in vitamin C.
Patients should limit the intake of honey, sugar, salt, confectionery, sweet pastries. There are a number of strictly prohibited products: canned food, alcohol, smoked food, fatty meats and fish, coffee, condiments, ice cream, very hot or very cold food.
With strict adherence to this diet within two months, the hyperemia and edema of the mucosa of the intestine become less pronounced, and the health of patients significantly improved.
Drug treatment of duodenopathy
To reduce the severity of endoscopic signs of duodenopathy using such medications, like proton pump inhibitors. These funds reduce, and then inhibit the production of hydrochloric acid. These include derivatives of omeprazole, rabeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole. Not less important are histamine receptors on the foundations of ranitidine, famotidine, cimetidine.
Among drugs of great importance are blockers of cholinergic receptors and non-selective m-anticholinergics. This aid, which also reduces the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid. Antacids required to protect the mucosa and recovery.
Antibiotic therapy aimed at the destruction of one of the main etiological factors of duodenopathy — microorganism Helicobacter pylori. The drugs of choice are amoxicillin, tetracycline, clarithromycin.
The duration of treatment is strictly individual. Monitoring the healing of pathology is carried out using a repeated fibrogastroduodenoscopy. With the disappearance of all endoscopic signs of inflammation the treatment is completed.