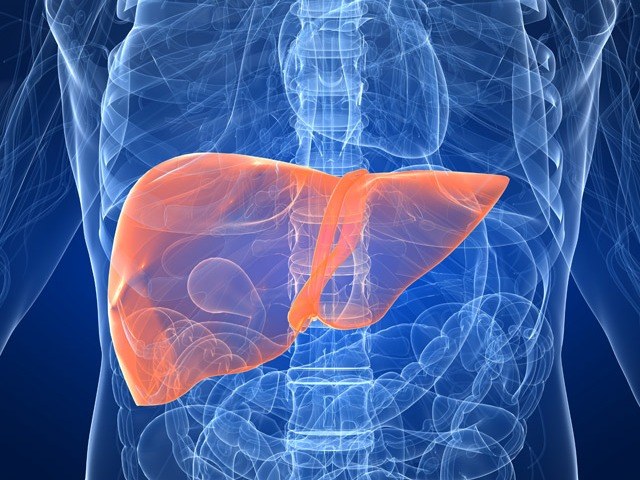
Hepatitis A is the most common type of hepatitis
The most common form is viral hepatitis type A (Botkin's disease). Virus diseases spread by casual contact, including through dirty hands, food or water contaminated with fecal material. From the moment of infection before occurrence of first symptoms (incubation period) may take 7-50 days. The disease begins with high fever, after 2-4 days in humans, urine darkens, and stool becomes colorless. Then develop jaundice, when it appears the patient's condition improves.
The duration of the disease can be from a week and a half to two months. During treatment, the patient is recommended bed rest, special diet, receiving hepatoprotectors - drugs that protect the liver. The recovery period after illness may take up to six months. Unlike other types of hepatitis a is the most favourable, it does not cause severe complications. The main measure to prevent this infection is hygiene, children are recommended vaccination.
Hepatitis b: modes of transmission, symptoms, the differences from hepatitis A
A much more dangerous disease is hepatitis b (serum hepatitis). It is characterized by severe liver damage. The causative agent of this disease is a virus that contains DNA. It can be transmitted through blood, sexual contact, there is a high probability of infection of the fetus from the mother.
The disease begins with weakness, fever, nausea and vomiting, pain in the joints. Can appear and other symptoms: discoloration of feces, dark urine, rash, enlarged liver and spleen. Unlike hepatitis A, hepatitis type b jaundice manoharachary. Liver damage can be severe in some cases may develop cirrhosis or cancer. In the treatment of disease using immune drugs, medications, hormones, antibiotics. As prevention hepatitis b vaccination is used.
Hepatitis C (hepatitis posttransfusion)
Hepatitis C is considered the most severe form of the disease. Most often it occurs in young people. Infection occurs mainly through blood – when using non-sterile needles or during blood transfusions. Infection transmitted sexually, the virus can also be transmitted from mother to fetus.
Approximately 70-80% of patients with hepatitis C develop a chronic form of the disease that represents the greatest danger, because it can cause malignant tumors or cirrhosis of the liver. If this type of hepatitis combined with other types of the disease, the patient's condition can rapidly deteriorate, even death. Currently a vaccine that can protect against infection With hepatitis C are not developed.