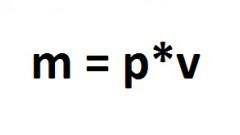You will need
- the linear density or the density of the material
Instruction
1
Units of mass are converted to units of length by using a physical quantity called linear density. In the SI system it has the dimension of kg/m. This value differs from the usual density that expresses the mass per unit volume.
Linear density is used to characterize the thickness of threads, wires, fabrics, etc., as well as for the characterization of beams, rails, etc.
Linear density is used to characterize the thickness of threads, wires, fabrics, etc., as well as for the characterization of beams, rails, etc.
2
From the definition of linear density, it follows that for the translation of the mass in the length needed to divide the weight in kilograms per linear density in kg/m this gives you the length in meters. This length will contain this mass.
3
In that case, if you are aware of the normal density with the dimension kg per cubic meter, to calculate the length of the material, which contains weight, you must first obtain a volume of material, encompassing the mass. To do this, divide the mass by the density. Then, the resulting amount is divided by the cross sectional area of the material. Thus, the formula for the length would be: l = V/S = (m/p*S) where m is the mass and V is the volume containing the mass, S is the cross - sectional area, p is the density.
4
In trivial cases, the cross section of the material will have either a round or rectangular shape. The area of the circular section is equal to pi*(R^2), where R is the radius of the cross section.
In the case of rectangular cross section, its area is equal to a*b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the section.
If the cross section has an irregular shape, then you need to find the area of the geometric shape in cross-section.
In the case of rectangular cross section, its area is equal to a*b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the section.
If the cross section has an irregular shape, then you need to find the area of the geometric shape in cross-section.