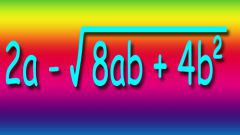Exponentiation implies that the given number must be multiplied by itself a certain number of times. For example, the construction of the number 2 in the fifth degree will be as follows:
2*2*2*2*2=64.
The number that should be multiplied by itself is called a basis of the degree and the number of multiplications is her figure. Exponentiation correspond to two opposite actions: finding rate and the finding of the base.
Finding the base of power is called the root. This means that you need to find the number that you want to build in a degree n to obtain this.
For example, you must remove the root of 4-th degree of the number 16, i.e., to determine what number to multiply on itself 4 times to get 16. This number – 2.
This arithmetic operation is written with a special sign of the radical: √, which is indicated on the left of the exponent.
If the exponent is an even number, the root may be two numbers with the same module, but with different signs – positive and negative. So, in the example it can be numbers 2 and -2.
The expression must be unambiguous, i.e. it must have one result. For this and introduced the concept of arithmetic root, which may be only positive number. To be less than zero, the arithmetic root can not.
Thus, in the above example, the arithmetic root is just the number 2, and the second answer is -2 is excluded by definition.
For some degrees, which are used most frequently in mathematics, there are special titles that are originally associated with the geometry. We are talking about the construction of the second and third degree.
Second degree erecting the side length of a square when you need to calculate its area. If you need to find the volume of a cube, the length of its edges raised to the third degree. Therefore, the second degree is called a square number, and the third cube.
Accordingly, the root of the second degree is called square, and the root of the third degree cubic. Square root – the only one of the roots, in which over a radical is the exponent:
√64=8
So, the arithmetic square root of a given number is a positive number, which is necessary to build in the second degree, to obtain the number.
2*2*2*2*2=64.
The number that should be multiplied by itself is called a basis of the degree and the number of multiplications is her figure. Exponentiation correspond to two opposite actions: finding rate and the finding of the base.
The root
Finding the base of power is called the root. This means that you need to find the number that you want to build in a degree n to obtain this.
For example, you must remove the root of 4-th degree of the number 16, i.e., to determine what number to multiply on itself 4 times to get 16. This number – 2.
This arithmetic operation is written with a special sign of the radical: √, which is indicated on the left of the exponent.
Arithmetic root
If the exponent is an even number, the root may be two numbers with the same module, but with different signs – positive and negative. So, in the example it can be numbers 2 and -2.
The expression must be unambiguous, i.e. it must have one result. For this and introduced the concept of arithmetic root, which may be only positive number. To be less than zero, the arithmetic root can not.
Thus, in the above example, the arithmetic root is just the number 2, and the second answer is -2 is excluded by definition.
Square root
For some degrees, which are used most frequently in mathematics, there are special titles that are originally associated with the geometry. We are talking about the construction of the second and third degree.
Second degree erecting the side length of a square when you need to calculate its area. If you need to find the volume of a cube, the length of its edges raised to the third degree. Therefore, the second degree is called a square number, and the third cube.
Accordingly, the root of the second degree is called square, and the root of the third degree cubic. Square root – the only one of the roots, in which over a radical is the exponent:
√64=8
So, the arithmetic square root of a given number is a positive number, which is necessary to build in the second degree, to obtain the number.