Stray currents typical for electrified railway and tram tracks, which are serviced improperly or accidental leakage from power lines. Sometimes such currents is called zero current, which exist in the grounded metal structures.
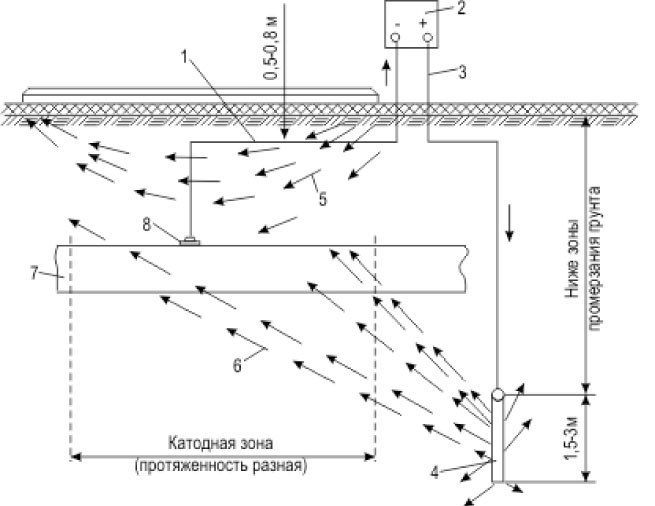
Sources of currents in the earth are underground, tram, electrified with direct current suburban rail transport. The wires in these types of transport are connected with a plus power source and a minus, with a return conductor rail tracks.
Because of poor isolation of the roadway from the ground, a large resistance of track, as well as violations of the joints of the rail, part of the current passes to the negative pole of the power source via earth. Meeting on the way the metal sheath of cables, pipelines and other underground structures, currents pass through these conduits and returning to the earth to get to minus traction substation.
Throughout this chain the path of the electric current there is a phenomenon of electrolysis. Where the metallic sheath of the cables and track are the electrodes (anode and cathode) and the damp soil containing large amounts of salts and acid – electrolytic environment (electrolyte). And if you move to DC current through the electrolyte, the electrode with higher potential dissolves.
Scientists have calculated that the magnitude of stray current in one ampere, in one year destroyed 33 pounds of lead, 3.95 kg aluminum and 9 pounds of iron. The strongest destruction of exposed lead sheath on the cable lines.
To protect underground structures and metal sheaths of cables from corrosion stray currents take special measures:
- as far as possible to reduce the resistance of the rail by welding of joints of rail and isolate the rail from the ground.
- to reduce the voltage drop in the rails using special line of the cable connecting different points of the rail with the negative bus of the substation.
These methods achieve significant unloading rail network and reduce the number of stray currents.
Sources of stray currents.
Sources of currents in the earth are underground, tram, electrified with direct current suburban rail transport. The wires in these types of transport are connected with a plus power source and a minus, with a return conductor rail tracks.
Products humus, alkali, lime, sour marshy soils containing lime, slag, ash creates conditions for intensive soil corrosion of the shells of metal.
Because of poor isolation of the roadway from the ground, a large resistance of track, as well as violations of the joints of the rail, part of the current passes to the negative pole of the power source via earth. Meeting on the way the metal sheath of cables, pipelines and other underground structures, currents pass through these conduits and returning to the earth to get to minus traction substation.
Throughout this chain the path of the electric current there is a phenomenon of electrolysis. Where the metallic sheath of the cables and track are the electrodes (anode and cathode) and the damp soil containing large amounts of salts and acid – electrolytic environment (electrolyte). And if you move to DC current through the electrolyte, the electrode with higher potential dissolves.
Electrolysis – the process of separating components of substances in solution, by passing electric current through it.
Scientists have calculated that the magnitude of stray current in one ampere, in one year destroyed 33 pounds of lead, 3.95 kg aluminum and 9 pounds of iron. The strongest destruction of exposed lead sheath on the cable lines.
Prevention of stray currents
To protect underground structures and metal sheaths of cables from corrosion stray currents take special measures:
- as far as possible to reduce the resistance of the rail by welding of joints of rail and isolate the rail from the ground.
- to reduce the voltage drop in the rails using special line of the cable connecting different points of the rail with the negative bus of the substation.
These methods achieve significant unloading rail network and reduce the number of stray currents.