You will need
- - cerebrospinal puncture;
- - puncture of jeludockove of the brain;
- - consultation of the ophthalmologist;
- - Ultrasound of the brain;
- CT.
Instruction
1
Increase cranial pressure accompanied by headache, severe nausea and vomiting, double vision and the emergence of flies in the eyes, weakness and fatigability. In addition, blood pressure becomes unstable, there is low-grade fever, etc., For confirmation of the signs of intracranial hypertension are diagnosed. There are direct and indirect methods of determining pressure. Increased intracranial pressure is necessarily accompanied by characteristic changes that are clearly visible during computer tomography, ultrasound of the brain, etc.
2
Direct methods for determining pressure include lumbar puncture cerebrospinal and brain ventricles. The procedures are quite complex and are carried out only according to strict indications when other diagnostics are ineffective.
3
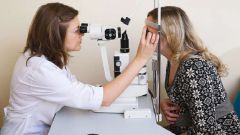
All other diagnostic methods include indirect methods of determining intracranial pressure. It is recommended that a fundus examination by a retinal specialist. Swelling of the optic disc and dilated veins of the retina of both eyes are signs that clearly indicate an increase in cranial pressure and provide a basis for further tests.
4
CT and magnetic resonance imaging show changes resulting from cranial hypertension is the thinning of brain tissue, increase the width of the ventricles of the brain, etc. To increase the accuracy of diagnosis before the procedure is introduced into the bloodstream of a special contrast agent that allows to clearly observe the blood vessels of the brain that are invisible in conventional imaging.
5
Electroencephalography allows to determine the bioelectric activity of the brain. Violation by a specialist of indicators serves as an indirect sign of intracranial hypertension.
6
Cerebral ultrasound to determine cranial hypertension is carried out only in children, not yet closed Fontanelle. Repeated examination of the width of the ventricles of the brain characterizes the changes in this index and is an indirect sign of cranial pressure, possibly hydrocephalus.
Note
Increased ICP requires urgent action, ranging from medical treatment to surgical intervention. The basis for emergency neurosurgical operation may be a skull fracture, epidural hematoma, or bleeding in the brain.