You will need
- A clean sheet, a pencil and a ruler to the diagram of the triangle.
Instruction
1
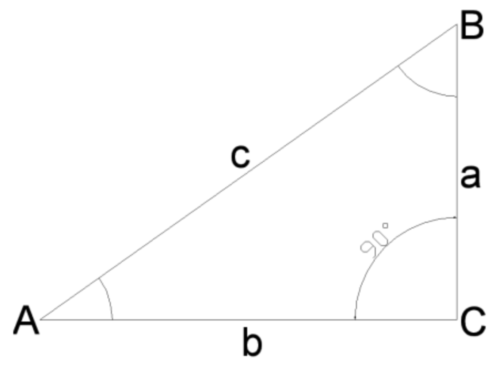
The triangle is rectangular if one of its angles equal to 90 degrees. It consists of two legs and a hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is called the great side of this triangle. It lies against the straight edge. The other two sides, respectively called the lower side of it. They can be equal and have different values. The equality of the legs means that you are working with an isosceles right triangle. The beauty of it is that it combines the properties of two shapes: rectangular and isosceles triangle. If the legs are not equal, then the triangle is arbitrary and obeys the basic law: the greater the angle, the more lying in front of him roll.
2
There are several ways of finding the hypotenuse leg and angle. But before you use one of them, you should determine what side and angle known. If given an angle and adjacent to it side, then the hypotenuse will be easier to find the cosine of the angle. The cosine of an acute angle (cos a) in a right triangle is the ratio of the adjacent leg to the hypotenuse. It follows that the hypotenuse (C) is equal to the ratio of adjacent sides (b) to the cosine of angle a (cos a). This can be written as: cos a=b/c => c=b/cos a.
3
If given angle and opposite side, it is necessary to work with the sine. The sine of an acute angle (a sin) in a right triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg (a) to the hypotenuse (c). There is a principle that in the previous example, but instead of cosine functions taken sinus. sin a=a/c => c=a/sin a.
4
You can also use a trigonometric function such as tangent. But finding unknown values is slightly more complicated. The tangent of an acute angle (tg a) in a right triangle is the ratio of the opposite leg (a) surrounding (b). Finding both of the leg, apply the Pythagorean theorem (the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides) and a large side of the triangle will be found.
Note
Working with the Pythagorean theorem, do not forget that you are dealing with a degree. Finding the sum of the squares of the other two sides, to obtain the final answer should be square root.