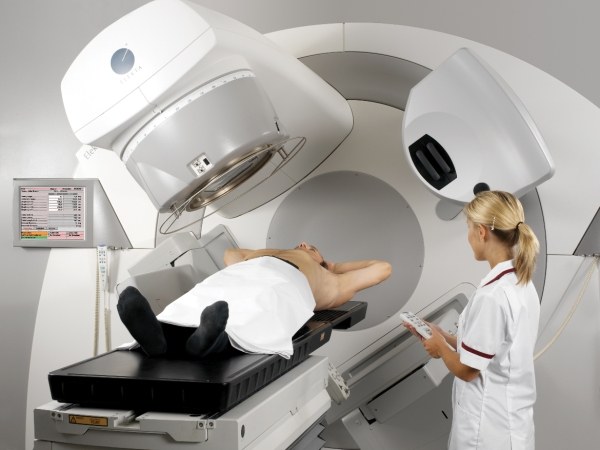
Radiation therapy - cancer treatment
Radiation therapy as a cancer treatment is widely used for several decades. It ensures the preservation of the body and its functions, reduces pain, improves survival rates and quality of life of the patient. The essence of radiation therapy is the use of high-energy ionizing radiation (wave and corpuscular). It is sent to the affected tumor area of the body. The principle of exposure is reduced to the reproductive abilities of cancer cells, as a result, the body gets rid of them naturally. Radiotherapy damages the cancer cells by the negative impact on their DNA, as a result, they become unable to divide and grow.
This method of treatment is the most effective for destroying rapidly dividing cells. Increased sensitivity of tumour cells to ionizing radiation due to 2 main factors: first, they divide much faster than healthy cells, and second, they cannot effectively repair the damage as normal cells. Radiotherapy is using the radiation source is a linear accelerator of charged particles. This device accelerates electrons and generates gamma rays or x-rays.
Some types of radiation therapy
Radiation for cancer is possible with radioactive sources placed into the patient (so-called internal radiation therapy or brachytherapy). In this case the radioactive material is inside of catheters, needles, special conductors, which are implanted inside the tumor or placed in close proximity to it. Brachytherapy is a common treatment for cancer of the prostate, cervix, uterus, breast. The radiation is so precisely effect inside the tumor, a negative impact on healthy organs is minimal.
Some patients have radiotherapy administered is surgical treatment, for example, for cancer of the larynx. In other cases, radiation therapy is only part of the treatment plan. If radiation is prescribed for cancer after surgery, called adjuvant. It is possible to perform radiotherapy before surgery; in this case it is called neoadjuvant, or induction. Such radiation therapy can facilitate the operation.