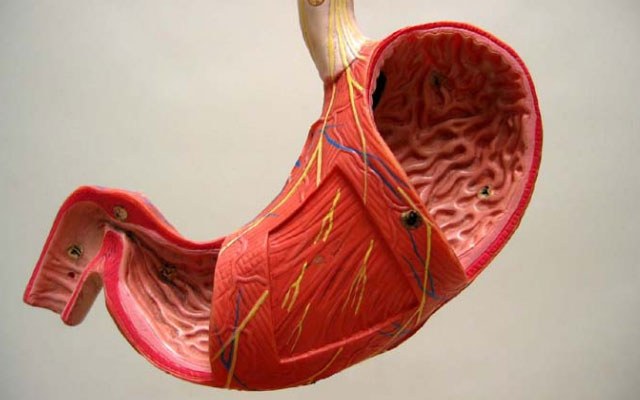
What is the size and shape of the stomach
The shape and size of the stomach is constantly changing depending on the amount of food eaten, the provisions of the human body. In addition, the shape of the stomach depends on the type of build. So, people brachymorphic type of physique the stomach is shaped like a horn and is situated almost transversely. People dolichomorphic type stomach resembles an elongated stocking, located almost vertically down and curving sharply to the right. Finally, if the type of mesomorphic physique, the stomach has the shape of a hook: its long axis is directed from top to bottom and left to right.
Length of an empty stomach in an adult is 18-20 cm, width 7-8 cm With moderate filling of the length of the body reaches 24-26 cm and a width of 10-12 cm is the Capacity of the stomach ranges from 1.5 to 4 liters.
Filled the stomach hinders and slows down digestion, so better to eat regularly in small portions.
What happens to food in the stomach
Food is crushed in the mouth and saturated with saliva, is retained in the stomach up to 4-6 hours. In this food mass is mixed and digested: the outer surface of the lumps of food is exposed to gastric juice, and the inside continues the action of saliva. Gradually food a lump disintegrates and turns into a slurry that has the whole is processed by the gastric juices. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes – pepsin, lipase. While the mucous glands secrete mucus that protects the stomach wall from the action of hydrochloric acid and irritating substances used for food. Absorbed in the stomach sugar, salt, water and alcohol.
Hydrochloric acid not only neutralizes penetrated with food microbes, but also creates the necessary environment for the pepsin – protein-digesting enzyme.
Where is the human stomach
The stomach is located in the upper part of the abdomen. With moderate filling three quarters of it lie in the left subcostal region, one quarter in adorable. When breath stomach may shift depending on the filling of the neighboring hollow organs, for example the transverse colon. Least movable input and output parts of the organ. Fixation of the stomach is provided by special folds of the peritoneum – ligaments: hepatic-gastric, gastro-colonic and gastro-splenic, gastro-phrenic, diaphragmatic-esophageal, privratnikovogo-pancreatic, stomach and pancreas.