Instruction
1
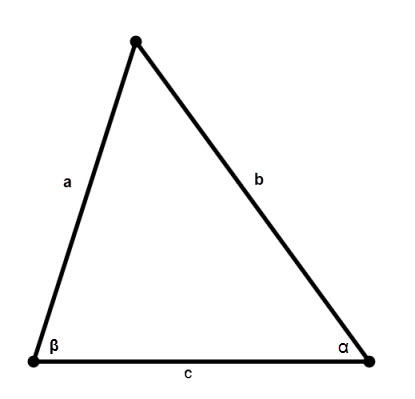
The area of each triangle can be calculated, knowing the length of its sides by Heron's formula:
S = √(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c)) where a ,b , c be the sidelengths of a triangle, p = (a + b + c)/2 – properiter.
S = √(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c)) where a ,b , c be the sidelengths of a triangle, p = (a + b + c)/2 – properiter.
2
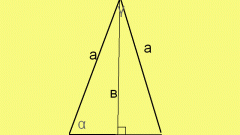
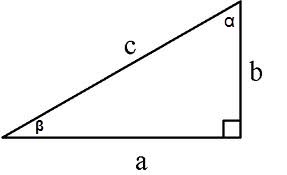
The area of a right triangle can be calculated in several ways:
1. On the two sides S = a * b/2, a, b are the legs
2. On the side, and opposite him a corner S = a2/2tg∠α,
3. On the side, and surrounding him with the corner S = (a2 * tg∠β)/2,
4. The leg and the hypotenuse is S = a * √(c2 - a2)/2, where c is the hypotenuse, a the side
5. The hypotenuse and adjacent to the corners
S = (c2 * sin∠α * cos∠α)/2 or S = (c2 * sin∠α * sin∠β)/2
1. On the two sides S = a * b/2, a, b are the legs
2. On the side, and opposite him a corner S = a2/2tg∠α,
3. On the side, and surrounding him with the corner S = (a2 * tg∠β)/2,
4. The leg and the hypotenuse is S = a * √(c2 - a2)/2, where c is the hypotenuse, a the side
5. The hypotenuse and adjacent to the corners
S = (c2 * sin∠α * cos∠α)/2 or S = (c2 * sin∠α * sin∠β)/2
3
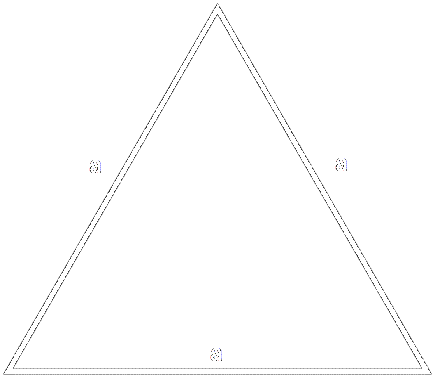
For equilateral triangles, the area can be calculated according to the formula
S = (a2 * √3)/4, where a is side of triangle
S = (a2 * √3)/4, where a is side of triangle
4
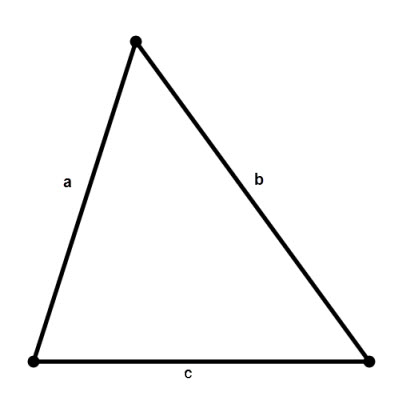
If in an arbitrary triangle one known side and two adjacent to the angle, its area is calculated according to the formulas
S = c2/(2 * (ctg∠α * ctg∠β)) or S = (c2 * sin∠α * sin∠β)/2 * sin(∠α + ∠β)
S = c2/(2 * (ctg∠α * ctg∠β)) or S = (c2 * sin∠α * sin∠β)/2 * sin(∠α + ∠β)