You will need
- - dental instruments:
- - x-ray.
Instruction
1
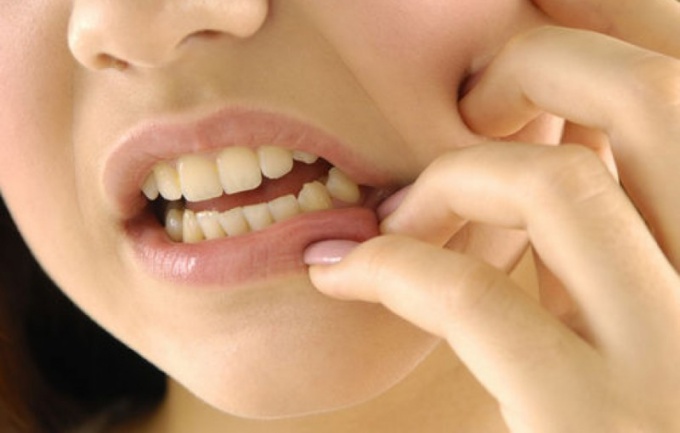
In the early stages of periostitis is manifested in the form of a nagging toothache. On the gums near the tooth appear solid sharply painful seal. Swelling becomes severe it spreads to the soft tissues of the face.
2
Depending on where the tooth, swollen lip, lower eyelid, cheek, or wing of the nose. Besides, increased body temperature is a response to infection, spreading of root canal of the tooth under the periosteum.
3
The bone rush of protective blood cells – leukocytes that break, forming purulent mass. The pus detaches the periosteum, causing inflammation of surrounding tissues and swelling.
4
After two or three days gingival mucosa becomes thinner, the pain decreases significantly after the release of the pus stops altogether. Simultaneously, the formation of the protective layer, which explains the thickening of the mucous membrane after the elimination of inflammation.
5
The flux can be chronic or acute. Abscess in the acute stage is serous inflammation of the periosteum. Palpation is accompanied by severe pain.
6
Without timely treatment, serous inflammation purulent go into. Of periodontal purulent exudate will penetrate under the periosteum. Body temperature in acute flux may rise up to 38.5 degrees.
7
Chronic abscess is a sluggish inflammation of the periosteum. The bone in the area of the affected tooth is thickened. The picture shows the x-ray region of the periosteum can be seen layered growths that alternate with foci of resorption.
Note
Running flux can lead to blood poisoning. In addition, the infection can reach the brain and contribute to the development of meningitis or inflammation of the meninges.
Useful advice
As a rule, the treatment of periodontitis involves the removal of the tooth the patient and concomitant therapy.