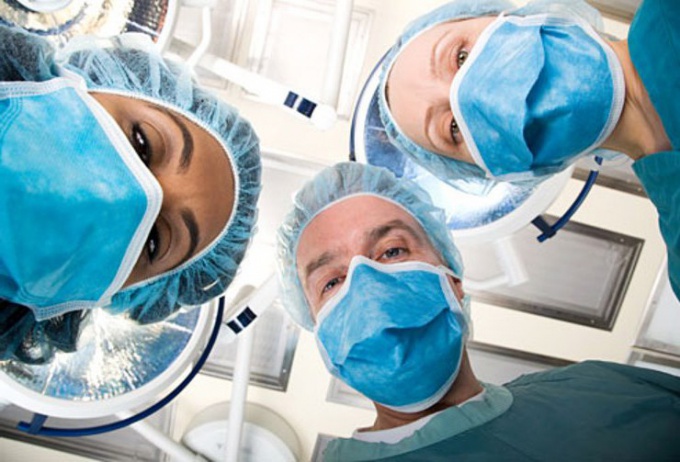
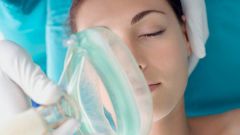
The anesthesiologist selects the anesthesia, the drugs and their optimal dose, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. Of great importance are the patient's age, his health, the nature of surgical intervention and individual drug tolerance.
General anesthesia is contraindicated in persons with severe allergies, predisposition to malignant hyperthermia, disorders of the cardiovascular system. During routine operations, a thorough examination of the patient and the risk of application of General anesthesia are minimized. However, this procedure cannot take place completely unnoticed and affect the body in a greater or lesser extent.
Nausea. Very common, about every third case. To reduce the risk of its occurrence, it is not necessary in the first hours after the surgery to sit and stand, can't drink and eat right after surgery.
Pain in the throat. Possible dry mouth, pain when swallowing, talking. These symptoms may remain for several days. If they do not pass more than three days, you should contact your doctor.
Shiver. This is a consequence of anesthesia is a temporary and often does not provide a danger.
Dizziness. The action of anesthetics can cause a decrease in blood pressure, which is manifested by dizziness, weakness, presyncope condition.
Headache. It can cause the drugs used for anesthesia, dehydration, surgery. Most often, the pain resolves on its own within a few hours after anesthesia. Severe headache can sometimes be a complication of spinal anesthesia or epidural anesthesia.
Back pain and lower back pain. These symptoms are caused, in most cases, prolonged stationary position during operation.
Confusion. In some patients, more often elderly, can cause impaired hearing and speech, hallucinations,
memory impairment, insomnia, confusion. Some children after General anesthesia can lag behind in development, but soon catching up with their peers. Usually, all these effects disappear with time.
Postoperative pulmonary infection. In some cases after anesthesia have symptoms of bronchitis or pneumonia. At risk are smokers, patients with chronic lung diseases.
Nerve damage. This type of complication is characterized by numbness, tingling, impaired sensation of heat or cold. You may feel weakness in limbs or paralysis. Injury to the nerve during epidural or spinal anesthesia are rare and often reversible injuries that take place in a few weeks.
Anaphylaxis. Drugs for anesthesia can cause severe allergic reaction – anaphylactic shock. The incidence of such complications is 1 :15000.
Death, brain damage. The risk increases in elderly persons, patients who have had a stroke, surgery on the brain, neck, heart or carotid arteries.
General anesthesia is contraindicated in persons with severe allergies, predisposition to malignant hyperthermia, disorders of the cardiovascular system. During routine operations, a thorough examination of the patient and the risk of application of General anesthesia are minimized. However, this procedure cannot take place completely unnoticed and affect the body in a greater or lesser extent.
Reversible effects of anesthesia
Nausea. Very common, about every third case. To reduce the risk of its occurrence, it is not necessary in the first hours after the surgery to sit and stand, can't drink and eat right after surgery.
Pain in the throat. Possible dry mouth, pain when swallowing, talking. These symptoms may remain for several days. If they do not pass more than three days, you should contact your doctor.
Shiver. This is a consequence of anesthesia is a temporary and often does not provide a danger.
Dizziness. The action of anesthetics can cause a decrease in blood pressure, which is manifested by dizziness, weakness, presyncope condition.
Headache. It can cause the drugs used for anesthesia, dehydration, surgery. Most often, the pain resolves on its own within a few hours after anesthesia. Severe headache can sometimes be a complication of spinal anesthesia or epidural anesthesia.
Back pain and lower back pain. These symptoms are caused, in most cases, prolonged stationary position during operation.
Confusion. In some patients, more often elderly, can cause impaired hearing and speech, hallucinations,
memory impairment, insomnia, confusion. Some children after General anesthesia can lag behind in development, but soon catching up with their peers. Usually, all these effects disappear with time.
Complications of anesthesia
Postoperative pulmonary infection. In some cases after anesthesia have symptoms of bronchitis or pneumonia. At risk are smokers, patients with chronic lung diseases.
Nerve damage. This type of complication is characterized by numbness, tingling, impaired sensation of heat or cold. You may feel weakness in limbs or paralysis. Injury to the nerve during epidural or spinal anesthesia are rare and often reversible injuries that take place in a few weeks.
Anaphylaxis. Drugs for anesthesia can cause severe allergic reaction – anaphylactic shock. The incidence of such complications is 1 :15000.
Death, brain damage. The risk increases in elderly persons, patients who have had a stroke, surgery on the brain, neck, heart or carotid arteries.