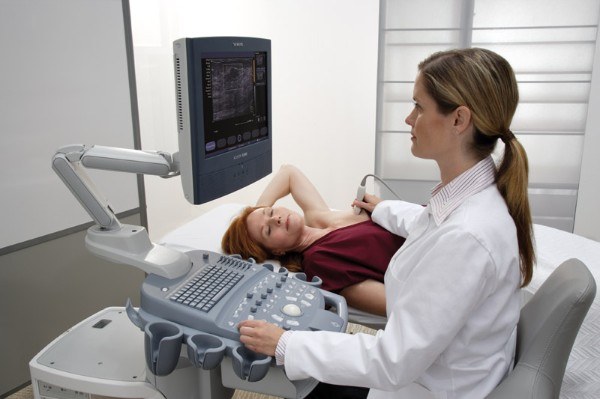
The term hypoechoic education" came into use with the advent of medical techniques ultrasound. As you know, during the procedure, ultrasound machine generates and sends to the studied organs high-frequency sound vibrations. Bodies in turn form the reflected ultrasound, which is in the form of an echo returns, perceived by the sensor device and converted into a picture on the monitor screen. Evaluation of the obtained data allows to draw the right conclusions about the state of organs and tissues.
With the help of ultrasound we can evaluate not only the location and size of the body, but also its structure. This introduces the concept of acoustic density or echogenicity, which means the speed of ultrasonic waves in the tissue or organ. Each on its value of acoustic density.
Hypoechoic education is a part of the body with reduced acoustic density, in which ultrasonic waves move slower than the surrounding space. The picture shows such a plot is considerably darker than the other structures.
Most often hypoechoic education – this cavity with thin walls, inside of which is a liquid. Such education can take various forms and contours and arranged in a variety of organs: the uterus, thyroid and mammary glands, liver, kidneys, ovaries.
During the ultrasound the doctor not only finds education with reduced density, but describes in detail what it looks like. If the structure is jagged, it could be a cyst, a tumor, a fibroadenoma and adenos breast cancer. The structure of rounded shape with smooth edges is often normal or parasitic cysts, tumor, galactocele in the mammary gland during lactation or follicle, if the investigation of the ovaries at mid-cycle.
Detected hypoechogenic formation may be any kind of pathology, but in any case, its presence suggests the need for more research. In particular, the doctor may prescribe biochemical analysis of blood and study using video-endoscopic techniques, ie, laparoscopy, bronchoscopy and cytoscopy. Sometimes requires a biopsy of an organ, which is accurate to 99% allows to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Characteristic hypoechogenic education
With the help of ultrasound we can evaluate not only the location and size of the body, but also its structure. This introduces the concept of acoustic density or echogenicity, which means the speed of ultrasonic waves in the tissue or organ. Each on its value of acoustic density.
Hypoechoic education is a part of the body with reduced acoustic density, in which ultrasonic waves move slower than the surrounding space. The picture shows such a plot is considerably darker than the other structures.
Most often hypoechoic education – this cavity with thin walls, inside of which is a liquid. Such education can take various forms and contours and arranged in a variety of organs: the uterus, thyroid and mammary glands, liver, kidneys, ovaries.
Which means the appearance of a hypoechogenic education
During the ultrasound the doctor not only finds education with reduced density, but describes in detail what it looks like. If the structure is jagged, it could be a cyst, a tumor, a fibroadenoma and adenos breast cancer. The structure of rounded shape with smooth edges is often normal or parasitic cysts, tumor, galactocele in the mammary gland during lactation or follicle, if the investigation of the ovaries at mid-cycle.
Detected hypoechogenic formation may be any kind of pathology, but in any case, its presence suggests the need for more research. In particular, the doctor may prescribe biochemical analysis of blood and study using video-endoscopic techniques, ie, laparoscopy, bronchoscopy and cytoscopy. Sometimes requires a biopsy of an organ, which is accurate to 99% allows to confirm or refute the diagnosis.