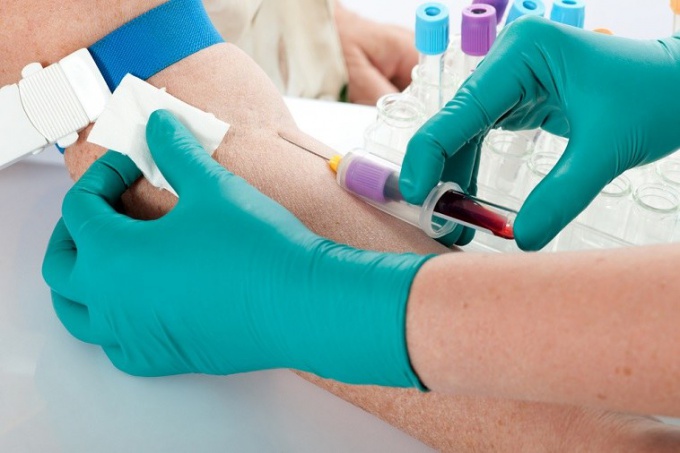
General analysis of blood
The study assigned all patients before surgery. Deviation of its results from the norm may be cause for rejection of the operation. One of the main indicators of this analysis is hemoglobin. When a low concentration of the patient is unlikely to be admitted to the operating room as a surgery involves significant blood loss. Threat may be an increased level of red blood cells, which dramatically increases the risk of postoperative thrombosis (blood clots). The increase in leukocyte count and ESR indicates the presence of infection in the body.
Urinalysis
The increase in the number of leukocytes and epithelial cells is a symptom of pyelonephritis and cystitis. Detection of red blood cells and protein in the urine - a symptom lesions of the renal tissue. However, if the deviation of these indicators from norms the decision on the surgery will depend on the disease and General condition of the patient.
Biochemical analysis of blood
Denial of surgical intervention, the patient may receive at a significantly elevated level of transaminases and bilirubin (liver disease), glucose (diabetes), creatinine (renal pathology) and electrolytes (heart disease). Signs of disorders of lipid metabolism (increased cholesterol) and slight variations in analysis are not the reason for the cancellation of a planned intervention.
Coagulation
The analysis on blood coagulation is very important to eliminate the possibility of bleeding or thrombosis. When performing abdominal surgery, the surgeon should be aware of the likelihood of complications during operation or after its completion.
The blood test for infection
The analysis for syphilis, viral hepatitis and HIV infection is mandatory before abdominal surgery. In the presence of his results, the doctor will have information of how dangerous a patient for other patients and for medical staff.
Analysis on the blood group
This study is carried out for all patients whose treatment involves open heart surgery. Because during the procedure there is a risk of bleeding, which required transfusion of blood and its substitutes.
Instrumental methods of research
In addition to testing, the patient performed an electrocardiogram, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography of the internal organs. The integrated survey provides the opportunity to reduce the risk of surgical intervention, which is preparing the patient.